Question runtime environment
Since PrairieLearn executes your question code in an environment that is not fully user-controlled, it can be useful to have an understanding of exactly how PrairieLearn executes your code. This page discusses the environment where your code is executed in, including which third-party libraries are available and how to install your own.
General information
All server.py files for questions are executed in a Docker container created from the prairielearn/prairielearn image. This image includes the Python version that is bundled with the latest version of Miniconda, as well as the packages in images/plbase/python-requirements.txt. The only packages guaranteed to be installed are those listed in the requirements file.
To run a command line version of this Python environment, you may start it with the following command:
docker run -it --rm prairielearn/prairielearn /bin/bashInstalling libraries in your course
The quickest way to add custom libraries is to install them directly to your course. This will assume that you are comfortable using Git and Docker. If you are not familiar, it is recommended to follow the Installing PL for local development guide.
- Check out a copy of your course locally with Git, and make sure the main branch is up-to-date.
- Locate the package that you would like to install. You can find a list of all the available Python libraries at the Python Package Index.
- Install the package to your course's
serverFileCoursedirectory with the following command. Make sure to replace<path-to-course>and<library>with the absolute path to the course on your local computer and the library you wish to install, respectively.docker run -it --rm -v <path-to-course>:/course prairielearn/prairielearn pip3 install --target /course/serverFilesCourse <library> - Using Git, commit and push the new files that are now in your
serverFilesCoursedirectory.
After these steps, you should be able to import the library as normal in your server.py files.
Adding libraries to PrairieLearn
If a library is very large or requires specific dependencies, it may be infeasible to install a it directly in your course. In that case, you can open a pull request to add it to PrairieLearn's built-in dependencies. This should be used as a last resort and is subject to maintainer approval. Note that this process will take more time, as your change will have to be reviewed, merged, and deployed. So, only use this in cases where installing directly in your course did not work.
Locate the library and version on PyPI
PrairieLearn downloads all of its Python packages from the Python Package Index; your first step should be to locate the package and version you want. You can find the versions under "Release history" on the left. Most of the time the latest version should be chosen unless there is a specific need for an older release.
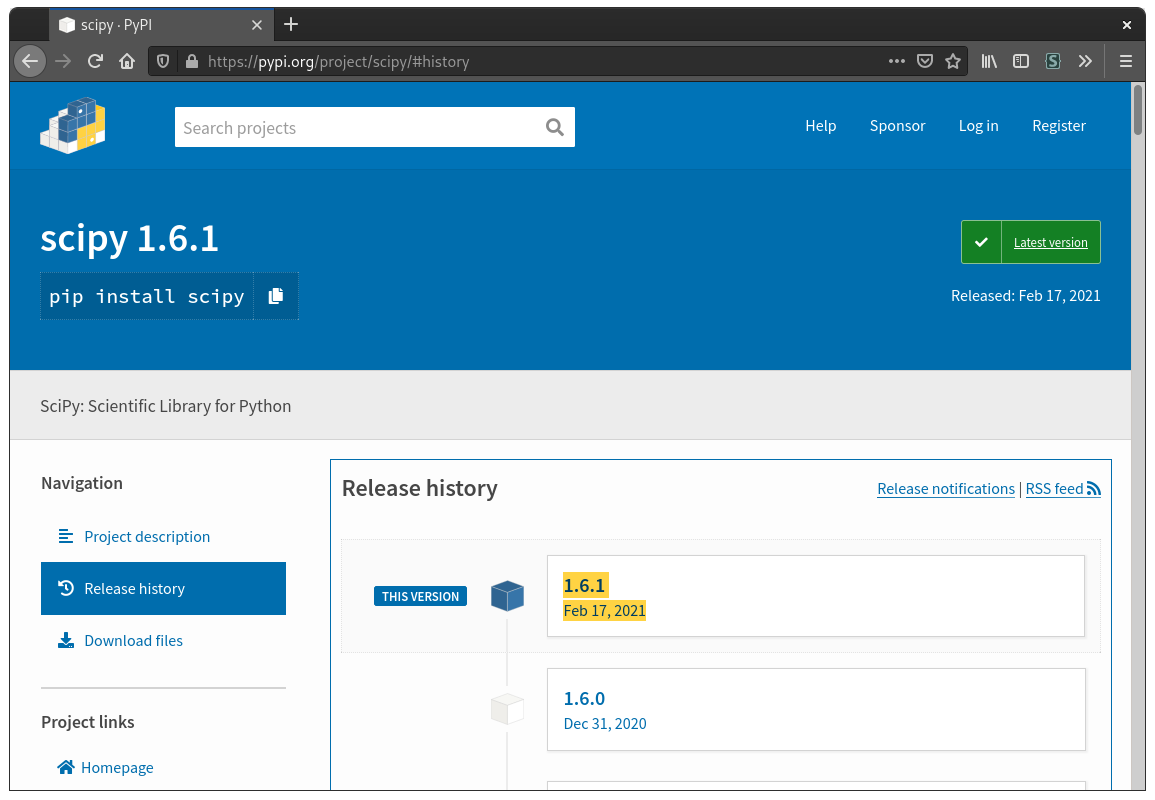 Example for SciPy. The newest release as of writing this guide is
Example for SciPy. The newest release as of writing this guide is 1.6.1.
Add the library to python-requirements.txt
A list of of the Python libraries that PrairieLearn uses is stored in a file called python-requirements.txt. The easiest way to propose a change to this file is to use the web interface (if you are familiar with Git and pull requests you may do that, but this will not be included for simplicity's sake).
First, browse to the file images/plbase/python-requirements.txt in the PL GitHub Repo. An edit button should be visible on the top right of the file preview:
Click the edit button to open a file editor. Add the new library and version on a new line in the format library==version, taking care to maintain alphabetical order in the file:
...
scikit-learn==1.3.0
+scipy==1.11.1
sphinx-markdown-builder==0.6.0
...When you're satisfied with your edits, click the "Commit changes..." button, enter a descriptive commit message, and click "Propose changes" to create the pull request.
Wait for review
If you've reached this point, then you're all finished! One of the PrairieLearn maintainers will look over your pull request shortly.